Attend Virtually$4,299.00
| Date | Day | Time | Duration |
| 21 Aug | Monday | 0900-17:00 ICT/GMT+7 | 8 Hours |
| 22 Aug | Tuesday | 0900-17:00 ICT/GMT+7 | 8 Hours |
| 23 Aug | Wednesday | 0900-17:00 ICT/GMT+7 | 8 Hours |
| 24 Aug | Thursday | 0900-17:00 ICT/GMT+7 | 8 Hours |
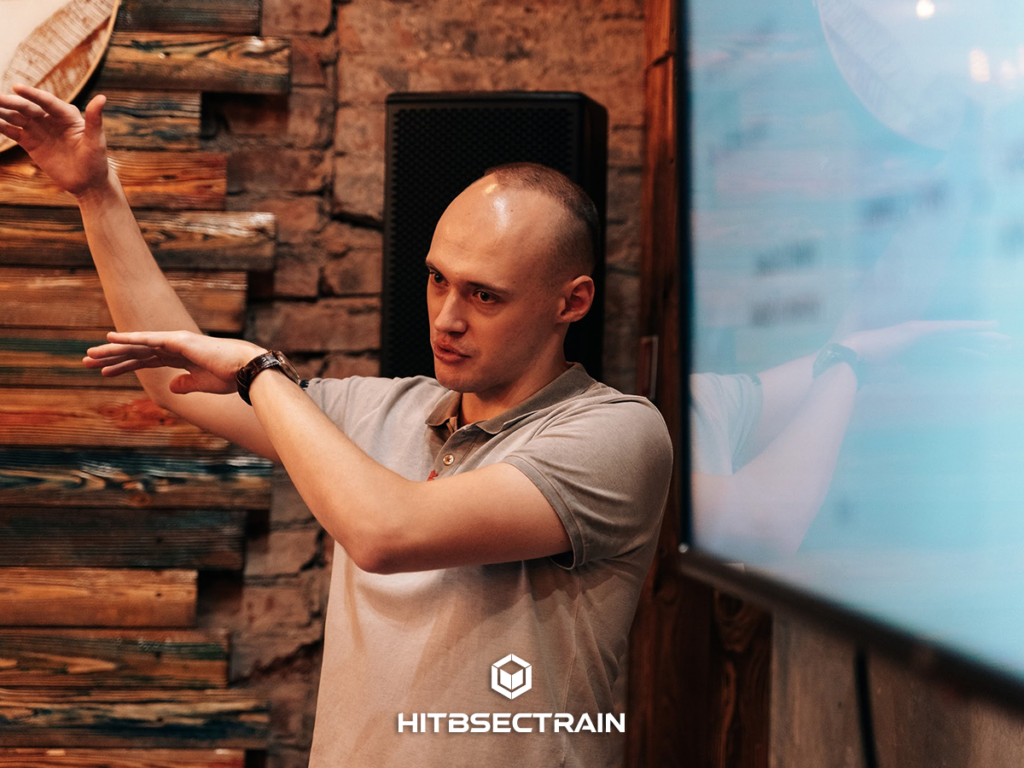
Besides providing a foundation for writing Linux kernel exploits, the training covers the no-less important areas of finding kernel bugs and evaluating their security impact. This includes chapters on using and extending dynamic bug-finding tools, writing custom fuzzers, and analyzing crashes.
The training starts with the beginner topics but proceeds into a few advanced areas as well.
A USB drive with: